Browse Articles
Display Method:
Display Method:
|
2024, 38(4): 543 -556
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0043-9
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
A multi-chamber oscillating water column wave energy converter (OWC-WEC) integrated to a breakwater is investigated. The hydrodynamic characteristics of the device are analyzed using an analytical model based on the linear potential flow theory. A pneumatic model is employed to investigate the relationship between the air mass flux in the chamber and the turbine characteristics. The effects of chamber width, wall draft and wall thickness on the hydrodynamic performance of a dual-chamber OWC-WEC are investigated. The results demonstrate that the device, with a smaller front wall draft and a wider rear chamber exhibits a broader effective frequency bandwidth. The device with a chamber-width-ratio of 1:3 performs better in terms of power absorption. Additionally, results from the analysis of a triple-chamber OWC-WEC demonstrate that reducing the front chamber width and increasing the rearward chamber width can improve the total performance of the device. Increasing the number of chambers from 1 to 2 or 3 can widen the effective frequency bandwidth.
2024, 38(4): 557 -571
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0044-8
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
To find a better way to estimate the lift force induced by an interceptor on a high-speed mono-hull ship, a series of high-speed mono-hull ship models are designed and investigated under different conditions. Different lift forces are obtained by numerical calculations and validated by a model test in a towing tank. The factors that influence the force are the interceptor height, velocity, draft, and deadrise angle. The relationship between each factor and the induced lift force is investigated and obtained. We found that the induced lift mainly depends on the interceptor height and advancing velocity, and is proportional to the square of the interceptor height and velocity. The results also showed that the effects of the draft and deadrise angle are relatively less important, and the relationship between the induced lift and these two factors is generally linear. Based on the results, a formula including the combined effect of all factors used to estimate the lift force induced by the interceptor is developed based on systematic analysis. The proposed formula could be used to estimate the lift force induced by interceptors, especially under high-speed condition.
2024, 38(4): 572 -585
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0045-7
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
Cryogenic valves play a crucial role in the production and transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG), and are primarily responsible for efficiently controlling the inflow and outflow of LNG and regulating pressure. However, due to their operation in low-temperature and high-humidity environments, crucial components such as drip trays are susceptible to frosting, which may lead to LNG leakage, thereby causing severe safety incidents. In this study, the user-defined function (UDF) is employed to redevelop Fluent, which integrates the frost growth model with the Eulerian multiphase flow model, to conduct a quantitative analysis of frosting on drip trays of cryogenic valves. The effects of environmental parameters, such as wind speed, ambient temperature, air humidity, and cold surface temperature on the growth of the frost layer were analyzed. This study reveals a limiting wind speed between 1 m/s and 2 m/s. Upon reaching this limit speed, the growth of the frost layer reaches its maximum, and further increases in the wind speed have no significant effect on the growth of the frost layer. Furthermore, the influence of the change in the flow field on droplet impingement and freezing during the growth of the frost layer is considered through the coupling method of the kinematic characteristics of water droplets and the collection coefficient of water droplets. This study identifies the influence of different parameters on the droplet impact efficiency, leading to the modification of the frost layer on the drip tray.
2024, 38(4): 586 -601
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0046-6
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
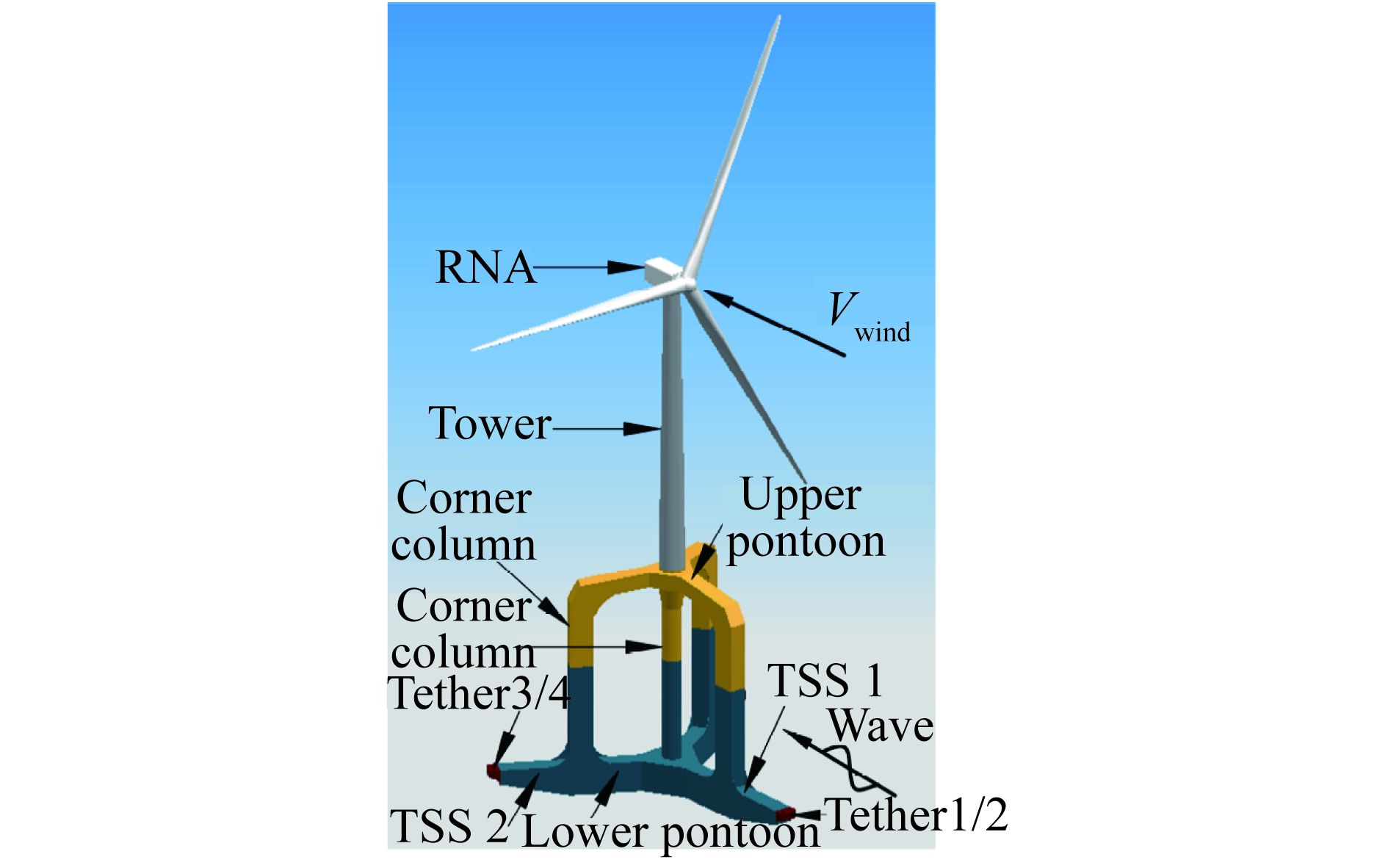
As offshore wind farms expand into deeper and farther ocean regions and the unit capacity of offshore wind turbines (OWTs) increases, there is a pressing need for a new foundation structure that can accommodate deep-sea conditions and support large capacities while maintaining economical and safe. To meet this goal of integrated transportation and one-step installation, a novel five-bucket jacket foundation (FBJF), with its suction installation and leveling methods in sand, has been proposed, analyzed and experimentally studied. First, seepage failure experiments of the FBJF at various depths were conducted, and a formula for calculating the critical suction of seepage failure suitable for the FBJF in sand was chosen and recommended for use with a range of values for the permeability coefficient ratio. Second, through leveling experiments of the FBJF at different depths, the maximum adjustable leveling angle during the sinking process was defined using seepage failure and the adjustable leveling angle of the foundation as control criteria. Various leveling control strategies were proposed and verified. Finally, an automatic sinking and leveling control system for the FBJF was developed and experimentally verified for feasibility.
2024, 38(4): 602 -611
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0047-5
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
A set of laboratory experiments are carried out to investigate the effect of following/opposing currents on wave attenuation. Rigid vegetation canopies with aligned and staggered configurations were tested under the condition of various regular wave heights and current velocities, with the constant water depth being 0.60 m to create the desired submerged scenarios. Results show that the vegetation-induced wave dissipation is enhanced with the increasing incident wave height. A larger velocity magnititude leads to a greater wave height attenuation for both following and opposing current conditions. Moreover, there is a strong positive linear correlation between the damping coefficient β and the relative wave height H0/h, especially for pure wave conditions. For the velocity profile, the distributions of Umin and Umax show different patterns under combined wave and current. The time-averaged turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) vary little under pure wave and Uc = ±0.05 m/s conditions. With the increase of flow velocity amplitude, the time-averaged TKE shows a particularly pronounced increase trend at the top of the canopy. The vegetation drag coefficients are obtained by a calibration approach. The empirical relations of drag coefficient with Reynolds and Keulegane−Carpenter numbers are proposed to further understand the wave-current-vegetation interaction mechanism.
2024, 38(4): 612 -624
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0048-4
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
In an effort to investigate and quantify the patterns of local scour, researchers embarked on an in-depth study using a systematic experimental approach. The research focused on the effects of local scour around a set of four piles, each subjected to different hydromechanical conditions. In particular, this study aimed to determine how different attack angles—the angles at which the water flow impinges on the piles, and gap ratios—the ratios of the spacing between the piles to their diameters, influence the extent and nature of scour. A comprehensive series of 35 carefully designed experiments were orchestrated, each designed to dissect the nuances in how the gap ratio and attack angle might contribute to changes in the local scour observed at the base of pile groups. During these experimental trials, a wealth of local scour data were collected to support the analysis. These data included precise topographic profiles of the sediment bed around the pile groups, as well as detailed scour time histories showing the evolution of scour at strategic feature points throughout the test procedure. The analysis of the experimental data provided interesting insights. The study revealed that the interplay between the gap ratio and the attack angle had a pronounced influence on the scouring dynamics of the pile groups. One of the key observations was that the initial phases of scour, particularly within the first hour of water flow exposure, were characterized by a sharp increase in the scour depth occurring immediately in front of the piles. After this initial rapid development, the scour depth transitioned to a more gradual change rate. In contrast, the scour topography around the piles continuously evolved. This suggests that sediment displacement and the associated sculpting of the seabed around pile foundations are sustained and progressive processes, altering the underwater landscape over time. The results of this empirical investigation have significant implications for the design and construction of offshore multi-pile foundations, providing a critical reference for engineers and designers to estimate the expected scour depth around such structures, which is an integral part of decisions regarding foundation design, selection of structural materials, and implementation of scour protection measures.
2024, 38(4): 625 -635
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0049-3
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
A new scour countermeasure using solidified slurry for offshore foundation has been proposed recently. Fluidized solidified slurry is pumped to seabed area around foundation for scour protection or pumped into the developed scour holes for scour repair as the fluidized material solidifies gradually. In the pumping operation and solidification, the engineering behaviors of solidified slurry require to be considered synthetically for the reliable application in scour repair and protection of ocean engineering such as the pumpability related flow value, flow diffusion behavior related rheological property, anti-scour performance related retention rate in solidification and bearing capacity related strength property after solidification. In this study, a series of laboratory tests are conducted to investigate the effects of mix proportion (initial water content and binder content) on the flow value, rheological properties, density, retention rate of solidified slurry and unconfined compressive strength (UCS). The results reveal that the flow value increases with the water content and decreases with the binder amount. All the solidified slurry exhibits Bingham plastic behavior when the shear rate is larger than 5 s−1. The Bingham model has been employed to fit the rheology test results, and empirical formulas for obtaining the density, yield stress and viscosity are established, providing scientific support for the numerical assessment of flow and diffusion of solidified slurry. Retention rate of solidified slurry decreases with the water flow velocity and flow value, which means the pumpability of solidified slurry is contrary to anti-scour performance. The unconfined compressive strength after solidification reduces as the water content increases and binder content decreases. A design and application procedure of solidified soil for scour repair and protection is also proposed for engineering reference.
2024, 38(4): 636 -647
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0050-x
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
A dent is a common type of defects for submarine pipeline. For submarine pipelines, high hydrostatic pressure and internal pressure are the main loads. Once pipelines bend due to complex subsea conditions, the compression strain capacity may be exceeded. Research into the local buckling failure and accurate prediction of the compressive strain capacity are important. A finite element model of a pipeline with a dent is established. Local buckling failure under a bending moment is investigated, and the compressive strain capacity is calculated. The effects of different parameters on pipeline local buckling are analyzed. The results show that the dent depth, external pressure and internal pressure lead to different local buckling failure modes of the pipeline. A higher internal pressure indicates a larger compressive strain capacity, and the opposite is true for external pressure. When the ratio of external pressure to collapse pressure of intact pipeline is greater than 0.1, the deeper the dent, the greater the compressive strain capacity of the pipeline. And as the ratio is less than 0.1, the opposite is true. On the basis of these results, a regression equation for predicting the compressive strain capacity of a dented submarine pipeline is proposed, which can be referred to during the integrity assessment of a submarine pipeline.
2024, 38(4): 648 -662
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0052-8
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Launching and recovering human-occupied vehicles (HOVs) has always been a challenging problem. The current recovery process requires staff to manually complete the tethering task, which is inefficient and endangers the lives of staff. This paper suggests moving the recovery position from the surface to underwater at approximately half the wavelength of the water depth (30−50 m underwater), where the HOV experiences less environmental disturbance. An ROV equipped with a ultra-short baseline beacon (USBL) and a manipulator was used to complete the tethering operation. Additionally, a shackle customized to the shape of the manipulator’s gripper is fitted to the end of the cable to simplify the tethering process. To investigate the dynamic response of recovering the HOV using this suggested method, a comprehensive numerical model is developed in this research. The effects of wind, surface waves, ocean currents, and nonlinear interaction between the installation vessel and the HOV are quantitatively examined. The results show that the proposed recovery method can reduce the motion amplitude of the HOV and that the wave has the greatest influence on the dynamic response of the HOV during the recovery process. This model provides better insight into the proposed HOV recovery method and confirms the effectiveness of the heave compensation system. The proposed approach aims to enhance safety and operational efficiency by reducing direct human involvement in the recovery process and mitigating potential dangers. This finding holds particular significance, especially in environmentally sensitive areas, where reducing the impact on the surrounding ecosystem is crucial.
2024, 38(4): 663 -675
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0051-9
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Two-dimensional (2D) flume experiments are useful in investigating the performances of floating breakwaters (FBs), including hydrodynamic performances, motion responses, and mooring forces. Designing a reasonable gap between the flume wall and the FBs is a critical step in 2D flume tests. However, research on the effect of the gap on the accuracy of 2D FB experimental results is scarce. To address this issue, a numerical wave tank is developed using CFD to estimate the wave-FB interaction of a moored dual-cylindrical FB, and the results are compared to experimental data from a previously published work. There is good agreement between them, indicating that the numerical model is sufficiently accurate. The numerical model is then applied to explore the effect of gap diffraction on the performance of FBs in 2D experiments. It was discovered that the nondimensional gap length LGap/WPool should be smaller than 7.5% to ensure that the relative error of the transmission coefficient is smaller than 3%. The influence of the gap is also related to the entering wave properties, such as the wave height and period.
2024, 38(4): 676 -688
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0053-7
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
The Submerged Floating Tunnel (SFT) relies on a tensioned mooring system for precise positioning. The sudden breakage of a single cable can trigger an immediate alteration in the constraint conditions of the tube, inducing a transient heave response within the structure along with a transient increase in cable tension experienced by adjacent cables. In more severe cases, this may even lead to a progressive failure culminating in the global destruction of the SFT. This study used ANSYS/AQWA to establish a numerical model of the entire length SFT for the hydrodynamic response analysis, and conducted a coupled calculation of the dynamic responses of the SFT-mooring line model based on OrcaFlex to study the global dynamic responses of the SFT at the moment of cable breakage and the redistribution of cable internal forces. The most unfavorable position for SFT cable breakage was identified, the influence mechanism of cable breakage at different positions on the global dynamic response was revealed, and the progressive chain failure pattern caused by localized cable breakage are also clarified.
2024, 38(4): 689 -700
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0054-6
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Salter’s duck, an asymmetrical wave energy converter (WEC) device, showed high efficiency in extracting energy from 2D regular waves in the past; yet, challenges remain for fluctuating wave conditions. These can potentially be addressed by adopting a negative stiffness mechanism (NSM) in WEC devices to enhance system efficiency, even in highly nonlinear and steep 3D waves. A weakly nonlinear model was developed which incorporated a nonlinear restoring moment and NSM into the linear formulations and was applied to an asymmetric WEC using a time domain potential flow model. The model was initially validated by comparing it with published experimental and numerical computational fluid dynamics results. The current results were in good agreement with the published results. It was found that the energy extraction increased in the range of 6% to 17% during the evaluation of the effectiveness of the NSM in regular waves. Under irregular wave conditions, specifically at the design wave conditions for the selected test site, the energy extraction increased by 2.4%, with annual energy production increments of approximately 0.8 MWh. The findings highlight the potential of NSM in enhancing the performance of asymmetric WEC devices, indicating more efficient energy extraction under various wave conditions.
2024, 38(4): 701 -710
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0055-5
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
The previous study conducted by Li (2022) demonstrates that the Goda graph can be adequately represented by a solitary-wave-like form across the entire range of relative water depth, with the exception of the extremely shallow zone. However, it remains uncertain whether this form is equally effective when applied to test data generated by irregular waves, as the Goda graph was initially developed based on overtopping data from regular wave tests. Additionally, it is unclear whether this form is suitable for formulating overtopping discharge at composite vertical walls. In order to address these questions, a 2D overtopping experiment was conducted, incorporating both simple and composite types of vertical walls, with various relative water depths across the entire range, excluding the extremely shallow zone. A novel analysis procedure was developed, which proved to be highly productive and can be considered a general method for data fitting. Ultimately, the study yielded two conclusions: (1) the solitary-wave-like form is remarkably effective in formulating overtopping test data generated by irregular waves, regardless of whether the vertical wall is simple or composite, and (2) the resulting formulas exhibit definitely better performance compared with existing formulas.
2024, 38(4): 711 -724
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0056-4
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Ocean waves and Stokes drift are generated by typhoons. This study investigated the characteristics of ocean waves and wave-induced Stokes drift and their effects during Typhoon Mangkhut using European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA5 datasets and observational data. The results revealed that the typhoon generated intense cyclones and huge typhoon waves with a maximum wind speed of 45 m/s, a minimum pressure of 955 hPa, and a maximum significant wave height of 12 m. The Stokes drift caused by typhoon waves exceeded 0.6 m/s, the Stokes depth scale exceeded 18 m, and the maximum Stokes transport reached 6 m2/s. The spatial distribution of 10-m wind speed, typhoon wave height, Stokes drift, Stokes depth, and Stokes transport during the typhoon was highly correlated with the typhoon track. The distribution along the typhoon track showed significant zonal asymmetry, with greater intensity on the right side of the typhoon track than on the left side. These findings provide important insights into the impact of typhoons on ocean waves and Stokes drift, thus improving our understanding of the interactions between typhoons and the ocean environment. This study also investigated the contribution of Stokes transport to the total net transport during typhoons using Ekman-Stokes Numbers as a comparative measure. The results indicated that the ratio of Stokes transport to the total net transport reached up to 50% within the typhoon radius, while it was approximately 30% outside the radius. Strong Stokes transport induced by typhoon waves led to divergence in the transport direction, which resulted in upwelling of the lower ocean as a compensation current. Thus, Stokes transport played a crucial role in the vertical mixing of the ocean during typhoons. The findings suggested that Stokes transport should be paid more attention to, particularly in high latitude ocean regions, where strong winds can amplify its effects.
Display Method:
Display Method: |
2024, 38(4): 543 -556
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0043-9
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
A multi-chamber oscillating water column wave energy converter (OWC-WEC) integrated to a breakwater is investigated. The hydrodynamic characteristics of the device are analyzed using an analytical model based on the linear potential flow theory. A pneumatic model is employed to investigate the relationship between the air mass flux in the chamber and the turbine characteristics. The effects of chamber width, wall draft and wall thickness on the hydrodynamic performance of a dual-chamber OWC-WEC are investigated. The results demonstrate that the device, with a smaller front wall draft and a wider rear chamber exhibits a broader effective frequency bandwidth. The device with a chamber-width-ratio of 1:3 performs better in terms of power absorption. Additionally, results from the analysis of a triple-chamber OWC-WEC demonstrate that reducing the front chamber width and increasing the rearward chamber width can improve the total performance of the device. Increasing the number of chambers from 1 to 2 or 3 can widen the effective frequency bandwidth.
A multi-chamber oscillating water column wave energy converter (OWC-WEC) integrated to a breakwater is investigated. The hydrodynamic characteristics of the device are analyzed using an analytical model based on the linear potential flow theory. A pneumatic model is employed to investigate the relationship between the air mass flux in the chamber and the turbine characteristics. The effects of chamber width, wall draft and wall thickness on the hydrodynamic performance of a dual-chamber OWC-WEC are investigated. The results demonstrate that the device, with a smaller front wall draft and a wider rear chamber exhibits a broader effective frequency bandwidth. The device with a chamber-width-ratio of 1:3 performs better in terms of power absorption. Additionally, results from the analysis of a triple-chamber OWC-WEC demonstrate that reducing the front chamber width and increasing the rearward chamber width can improve the total performance of the device. Increasing the number of chambers from 1 to 2 or 3 can widen the effective frequency bandwidth.
2024, 38(4): 557 -571
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0044-8
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
To find a better way to estimate the lift force induced by an interceptor on a high-speed mono-hull ship, a series of high-speed mono-hull ship models are designed and investigated under different conditions. Different lift forces are obtained by numerical calculations and validated by a model test in a towing tank. The factors that influence the force are the interceptor height, velocity, draft, and deadrise angle. The relationship between each factor and the induced lift force is investigated and obtained. We found that the induced lift mainly depends on the interceptor height and advancing velocity, and is proportional to the square of the interceptor height and velocity. The results also showed that the effects of the draft and deadrise angle are relatively less important, and the relationship between the induced lift and these two factors is generally linear. Based on the results, a formula including the combined effect of all factors used to estimate the lift force induced by the interceptor is developed based on systematic analysis. The proposed formula could be used to estimate the lift force induced by interceptors, especially under high-speed condition.
To find a better way to estimate the lift force induced by an interceptor on a high-speed mono-hull ship, a series of high-speed mono-hull ship models are designed and investigated under different conditions. Different lift forces are obtained by numerical calculations and validated by a model test in a towing tank. The factors that influence the force are the interceptor height, velocity, draft, and deadrise angle. The relationship between each factor and the induced lift force is investigated and obtained. We found that the induced lift mainly depends on the interceptor height and advancing velocity, and is proportional to the square of the interceptor height and velocity. The results also showed that the effects of the draft and deadrise angle are relatively less important, and the relationship between the induced lift and these two factors is generally linear. Based on the results, a formula including the combined effect of all factors used to estimate the lift force induced by the interceptor is developed based on systematic analysis. The proposed formula could be used to estimate the lift force induced by interceptors, especially under high-speed condition.
2024, 38(4): 572 -585
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0045-7
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
Cryogenic valves play a crucial role in the production and transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG), and are primarily responsible for efficiently controlling the inflow and outflow of LNG and regulating pressure. However, due to their operation in low-temperature and high-humidity environments, crucial components such as drip trays are susceptible to frosting, which may lead to LNG leakage, thereby causing severe safety incidents. In this study, the user-defined function (UDF) is employed to redevelop Fluent, which integrates the frost growth model with the Eulerian multiphase flow model, to conduct a quantitative analysis of frosting on drip trays of cryogenic valves. The effects of environmental parameters, such as wind speed, ambient temperature, air humidity, and cold surface temperature on the growth of the frost layer were analyzed. This study reveals a limiting wind speed between 1 m/s and 2 m/s. Upon reaching this limit speed, the growth of the frost layer reaches its maximum, and further increases in the wind speed have no significant effect on the growth of the frost layer. Furthermore, the influence of the change in the flow field on droplet impingement and freezing during the growth of the frost layer is considered through the coupling method of the kinematic characteristics of water droplets and the collection coefficient of water droplets. This study identifies the influence of different parameters on the droplet impact efficiency, leading to the modification of the frost layer on the drip tray.
Cryogenic valves play a crucial role in the production and transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG), and are primarily responsible for efficiently controlling the inflow and outflow of LNG and regulating pressure. However, due to their operation in low-temperature and high-humidity environments, crucial components such as drip trays are susceptible to frosting, which may lead to LNG leakage, thereby causing severe safety incidents. In this study, the user-defined function (UDF) is employed to redevelop Fluent, which integrates the frost growth model with the Eulerian multiphase flow model, to conduct a quantitative analysis of frosting on drip trays of cryogenic valves. The effects of environmental parameters, such as wind speed, ambient temperature, air humidity, and cold surface temperature on the growth of the frost layer were analyzed. This study reveals a limiting wind speed between 1 m/s and 2 m/s. Upon reaching this limit speed, the growth of the frost layer reaches its maximum, and further increases in the wind speed have no significant effect on the growth of the frost layer. Furthermore, the influence of the change in the flow field on droplet impingement and freezing during the growth of the frost layer is considered through the coupling method of the kinematic characteristics of water droplets and the collection coefficient of water droplets. This study identifies the influence of different parameters on the droplet impact efficiency, leading to the modification of the frost layer on the drip tray.
2024, 38(4): 586 -601
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0046-6
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
As offshore wind farms expand into deeper and farther ocean regions and the unit capacity of offshore wind turbines (OWTs) increases, there is a pressing need for a new foundation structure that can accommodate deep-sea conditions and support large capacities while maintaining economical and safe. To meet this goal of integrated transportation and one-step installation, a novel five-bucket jacket foundation (FBJF), with its suction installation and leveling methods in sand, has been proposed, analyzed and experimentally studied. First, seepage failure experiments of the FBJF at various depths were conducted, and a formula for calculating the critical suction of seepage failure suitable for the FBJF in sand was chosen and recommended for use with a range of values for the permeability coefficient ratio. Second, through leveling experiments of the FBJF at different depths, the maximum adjustable leveling angle during the sinking process was defined using seepage failure and the adjustable leveling angle of the foundation as control criteria. Various leveling control strategies were proposed and verified. Finally, an automatic sinking and leveling control system for the FBJF was developed and experimentally verified for feasibility.
As offshore wind farms expand into deeper and farther ocean regions and the unit capacity of offshore wind turbines (OWTs) increases, there is a pressing need for a new foundation structure that can accommodate deep-sea conditions and support large capacities while maintaining economical and safe. To meet this goal of integrated transportation and one-step installation, a novel five-bucket jacket foundation (FBJF), with its suction installation and leveling methods in sand, has been proposed, analyzed and experimentally studied. First, seepage failure experiments of the FBJF at various depths were conducted, and a formula for calculating the critical suction of seepage failure suitable for the FBJF in sand was chosen and recommended for use with a range of values for the permeability coefficient ratio. Second, through leveling experiments of the FBJF at different depths, the maximum adjustable leveling angle during the sinking process was defined using seepage failure and the adjustable leveling angle of the foundation as control criteria. Various leveling control strategies were proposed and verified. Finally, an automatic sinking and leveling control system for the FBJF was developed and experimentally verified for feasibility.
2024, 38(4): 602 -611
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0047-5
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
A set of laboratory experiments are carried out to investigate the effect of following/opposing currents on wave attenuation. Rigid vegetation canopies with aligned and staggered configurations were tested under the condition of various regular wave heights and current velocities, with the constant water depth being 0.60 m to create the desired submerged scenarios. Results show that the vegetation-induced wave dissipation is enhanced with the increasing incident wave height. A larger velocity magnititude leads to a greater wave height attenuation for both following and opposing current conditions. Moreover, there is a strong positive linear correlation between the damping coefficient β and the relative wave height H0/h, especially for pure wave conditions. For the velocity profile, the distributions of Umin and Umax show different patterns under combined wave and current. The time-averaged turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) vary little under pure wave and Uc = ±0.05 m/s conditions. With the increase of flow velocity amplitude, the time-averaged TKE shows a particularly pronounced increase trend at the top of the canopy. The vegetation drag coefficients are obtained by a calibration approach. The empirical relations of drag coefficient with Reynolds and Keulegane−Carpenter numbers are proposed to further understand the wave-current-vegetation interaction mechanism.
A set of laboratory experiments are carried out to investigate the effect of following/opposing currents on wave attenuation. Rigid vegetation canopies with aligned and staggered configurations were tested under the condition of various regular wave heights and current velocities, with the constant water depth being 0.60 m to create the desired submerged scenarios. Results show that the vegetation-induced wave dissipation is enhanced with the increasing incident wave height. A larger velocity magnititude leads to a greater wave height attenuation for both following and opposing current conditions. Moreover, there is a strong positive linear correlation between the damping coefficient β and the relative wave height H0/h, especially for pure wave conditions. For the velocity profile, the distributions of Umin and Umax show different patterns under combined wave and current. The time-averaged turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) vary little under pure wave and Uc = ±0.05 m/s conditions. With the increase of flow velocity amplitude, the time-averaged TKE shows a particularly pronounced increase trend at the top of the canopy. The vegetation drag coefficients are obtained by a calibration approach. The empirical relations of drag coefficient with Reynolds and Keulegane−Carpenter numbers are proposed to further understand the wave-current-vegetation interaction mechanism.
2024, 38(4): 612 -624
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0048-4
[Abstract](1)
Abstract:
In an effort to investigate and quantify the patterns of local scour, researchers embarked on an in-depth study using a systematic experimental approach. The research focused on the effects of local scour around a set of four piles, each subjected to different hydromechanical conditions. In particular, this study aimed to determine how different attack angles—the angles at which the water flow impinges on the piles, and gap ratios—the ratios of the spacing between the piles to their diameters, influence the extent and nature of scour. A comprehensive series of 35 carefully designed experiments were orchestrated, each designed to dissect the nuances in how the gap ratio and attack angle might contribute to changes in the local scour observed at the base of pile groups. During these experimental trials, a wealth of local scour data were collected to support the analysis. These data included precise topographic profiles of the sediment bed around the pile groups, as well as detailed scour time histories showing the evolution of scour at strategic feature points throughout the test procedure. The analysis of the experimental data provided interesting insights. The study revealed that the interplay between the gap ratio and the attack angle had a pronounced influence on the scouring dynamics of the pile groups. One of the key observations was that the initial phases of scour, particularly within the first hour of water flow exposure, were characterized by a sharp increase in the scour depth occurring immediately in front of the piles. After this initial rapid development, the scour depth transitioned to a more gradual change rate. In contrast, the scour topography around the piles continuously evolved. This suggests that sediment displacement and the associated sculpting of the seabed around pile foundations are sustained and progressive processes, altering the underwater landscape over time. The results of this empirical investigation have significant implications for the design and construction of offshore multi-pile foundations, providing a critical reference for engineers and designers to estimate the expected scour depth around such structures, which is an integral part of decisions regarding foundation design, selection of structural materials, and implementation of scour protection measures.
In an effort to investigate and quantify the patterns of local scour, researchers embarked on an in-depth study using a systematic experimental approach. The research focused on the effects of local scour around a set of four piles, each subjected to different hydromechanical conditions. In particular, this study aimed to determine how different attack angles—the angles at which the water flow impinges on the piles, and gap ratios—the ratios of the spacing between the piles to their diameters, influence the extent and nature of scour. A comprehensive series of 35 carefully designed experiments were orchestrated, each designed to dissect the nuances in how the gap ratio and attack angle might contribute to changes in the local scour observed at the base of pile groups. During these experimental trials, a wealth of local scour data were collected to support the analysis. These data included precise topographic profiles of the sediment bed around the pile groups, as well as detailed scour time histories showing the evolution of scour at strategic feature points throughout the test procedure. The analysis of the experimental data provided interesting insights. The study revealed that the interplay between the gap ratio and the attack angle had a pronounced influence on the scouring dynamics of the pile groups. One of the key observations was that the initial phases of scour, particularly within the first hour of water flow exposure, were characterized by a sharp increase in the scour depth occurring immediately in front of the piles. After this initial rapid development, the scour depth transitioned to a more gradual change rate. In contrast, the scour topography around the piles continuously evolved. This suggests that sediment displacement and the associated sculpting of the seabed around pile foundations are sustained and progressive processes, altering the underwater landscape over time. The results of this empirical investigation have significant implications for the design and construction of offshore multi-pile foundations, providing a critical reference for engineers and designers to estimate the expected scour depth around such structures, which is an integral part of decisions regarding foundation design, selection of structural materials, and implementation of scour protection measures.
2024, 38(4): 625 -635
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0049-3
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
A new scour countermeasure using solidified slurry for offshore foundation has been proposed recently. Fluidized solidified slurry is pumped to seabed area around foundation for scour protection or pumped into the developed scour holes for scour repair as the fluidized material solidifies gradually. In the pumping operation and solidification, the engineering behaviors of solidified slurry require to be considered synthetically for the reliable application in scour repair and protection of ocean engineering such as the pumpability related flow value, flow diffusion behavior related rheological property, anti-scour performance related retention rate in solidification and bearing capacity related strength property after solidification. In this study, a series of laboratory tests are conducted to investigate the effects of mix proportion (initial water content and binder content) on the flow value, rheological properties, density, retention rate of solidified slurry and unconfined compressive strength (UCS). The results reveal that the flow value increases with the water content and decreases with the binder amount. All the solidified slurry exhibits Bingham plastic behavior when the shear rate is larger than 5 s−1. The Bingham model has been employed to fit the rheology test results, and empirical formulas for obtaining the density, yield stress and viscosity are established, providing scientific support for the numerical assessment of flow and diffusion of solidified slurry. Retention rate of solidified slurry decreases with the water flow velocity and flow value, which means the pumpability of solidified slurry is contrary to anti-scour performance. The unconfined compressive strength after solidification reduces as the water content increases and binder content decreases. A design and application procedure of solidified soil for scour repair and protection is also proposed for engineering reference.
A new scour countermeasure using solidified slurry for offshore foundation has been proposed recently. Fluidized solidified slurry is pumped to seabed area around foundation for scour protection or pumped into the developed scour holes for scour repair as the fluidized material solidifies gradually. In the pumping operation and solidification, the engineering behaviors of solidified slurry require to be considered synthetically for the reliable application in scour repair and protection of ocean engineering such as the pumpability related flow value, flow diffusion behavior related rheological property, anti-scour performance related retention rate in solidification and bearing capacity related strength property after solidification. In this study, a series of laboratory tests are conducted to investigate the effects of mix proportion (initial water content and binder content) on the flow value, rheological properties, density, retention rate of solidified slurry and unconfined compressive strength (UCS). The results reveal that the flow value increases with the water content and decreases with the binder amount. All the solidified slurry exhibits Bingham plastic behavior when the shear rate is larger than 5 s−1. The Bingham model has been employed to fit the rheology test results, and empirical formulas for obtaining the density, yield stress and viscosity are established, providing scientific support for the numerical assessment of flow and diffusion of solidified slurry. Retention rate of solidified slurry decreases with the water flow velocity and flow value, which means the pumpability of solidified slurry is contrary to anti-scour performance. The unconfined compressive strength after solidification reduces as the water content increases and binder content decreases. A design and application procedure of solidified soil for scour repair and protection is also proposed for engineering reference.
2024, 38(4): 636 -647
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0050-x
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
A dent is a common type of defects for submarine pipeline. For submarine pipelines, high hydrostatic pressure and internal pressure are the main loads. Once pipelines bend due to complex subsea conditions, the compression strain capacity may be exceeded. Research into the local buckling failure and accurate prediction of the compressive strain capacity are important. A finite element model of a pipeline with a dent is established. Local buckling failure under a bending moment is investigated, and the compressive strain capacity is calculated. The effects of different parameters on pipeline local buckling are analyzed. The results show that the dent depth, external pressure and internal pressure lead to different local buckling failure modes of the pipeline. A higher internal pressure indicates a larger compressive strain capacity, and the opposite is true for external pressure. When the ratio of external pressure to collapse pressure of intact pipeline is greater than 0.1, the deeper the dent, the greater the compressive strain capacity of the pipeline. And as the ratio is less than 0.1, the opposite is true. On the basis of these results, a regression equation for predicting the compressive strain capacity of a dented submarine pipeline is proposed, which can be referred to during the integrity assessment of a submarine pipeline.
A dent is a common type of defects for submarine pipeline. For submarine pipelines, high hydrostatic pressure and internal pressure are the main loads. Once pipelines bend due to complex subsea conditions, the compression strain capacity may be exceeded. Research into the local buckling failure and accurate prediction of the compressive strain capacity are important. A finite element model of a pipeline with a dent is established. Local buckling failure under a bending moment is investigated, and the compressive strain capacity is calculated. The effects of different parameters on pipeline local buckling are analyzed. The results show that the dent depth, external pressure and internal pressure lead to different local buckling failure modes of the pipeline. A higher internal pressure indicates a larger compressive strain capacity, and the opposite is true for external pressure. When the ratio of external pressure to collapse pressure of intact pipeline is greater than 0.1, the deeper the dent, the greater the compressive strain capacity of the pipeline. And as the ratio is less than 0.1, the opposite is true. On the basis of these results, a regression equation for predicting the compressive strain capacity of a dented submarine pipeline is proposed, which can be referred to during the integrity assessment of a submarine pipeline.
2024, 38(4): 648 -662
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0052-8
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Launching and recovering human-occupied vehicles (HOVs) has always been a challenging problem. The current recovery process requires staff to manually complete the tethering task, which is inefficient and endangers the lives of staff. This paper suggests moving the recovery position from the surface to underwater at approximately half the wavelength of the water depth (30−50 m underwater), where the HOV experiences less environmental disturbance. An ROV equipped with a ultra-short baseline beacon (USBL) and a manipulator was used to complete the tethering operation. Additionally, a shackle customized to the shape of the manipulator’s gripper is fitted to the end of the cable to simplify the tethering process. To investigate the dynamic response of recovering the HOV using this suggested method, a comprehensive numerical model is developed in this research. The effects of wind, surface waves, ocean currents, and nonlinear interaction between the installation vessel and the HOV are quantitatively examined. The results show that the proposed recovery method can reduce the motion amplitude of the HOV and that the wave has the greatest influence on the dynamic response of the HOV during the recovery process. This model provides better insight into the proposed HOV recovery method and confirms the effectiveness of the heave compensation system. The proposed approach aims to enhance safety and operational efficiency by reducing direct human involvement in the recovery process and mitigating potential dangers. This finding holds particular significance, especially in environmentally sensitive areas, where reducing the impact on the surrounding ecosystem is crucial.
Launching and recovering human-occupied vehicles (HOVs) has always been a challenging problem. The current recovery process requires staff to manually complete the tethering task, which is inefficient and endangers the lives of staff. This paper suggests moving the recovery position from the surface to underwater at approximately half the wavelength of the water depth (30−50 m underwater), where the HOV experiences less environmental disturbance. An ROV equipped with a ultra-short baseline beacon (USBL) and a manipulator was used to complete the tethering operation. Additionally, a shackle customized to the shape of the manipulator’s gripper is fitted to the end of the cable to simplify the tethering process. To investigate the dynamic response of recovering the HOV using this suggested method, a comprehensive numerical model is developed in this research. The effects of wind, surface waves, ocean currents, and nonlinear interaction between the installation vessel and the HOV are quantitatively examined. The results show that the proposed recovery method can reduce the motion amplitude of the HOV and that the wave has the greatest influence on the dynamic response of the HOV during the recovery process. This model provides better insight into the proposed HOV recovery method and confirms the effectiveness of the heave compensation system. The proposed approach aims to enhance safety and operational efficiency by reducing direct human involvement in the recovery process and mitigating potential dangers. This finding holds particular significance, especially in environmentally sensitive areas, where reducing the impact on the surrounding ecosystem is crucial.
2024, 38(4): 663 -675
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0051-9
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Two-dimensional (2D) flume experiments are useful in investigating the performances of floating breakwaters (FBs), including hydrodynamic performances, motion responses, and mooring forces. Designing a reasonable gap between the flume wall and the FBs is a critical step in 2D flume tests. However, research on the effect of the gap on the accuracy of 2D FB experimental results is scarce. To address this issue, a numerical wave tank is developed using CFD to estimate the wave-FB interaction of a moored dual-cylindrical FB, and the results are compared to experimental data from a previously published work. There is good agreement between them, indicating that the numerical model is sufficiently accurate. The numerical model is then applied to explore the effect of gap diffraction on the performance of FBs in 2D experiments. It was discovered that the nondimensional gap length LGap/WPool should be smaller than 7.5% to ensure that the relative error of the transmission coefficient is smaller than 3%. The influence of the gap is also related to the entering wave properties, such as the wave height and period.
Two-dimensional (2D) flume experiments are useful in investigating the performances of floating breakwaters (FBs), including hydrodynamic performances, motion responses, and mooring forces. Designing a reasonable gap between the flume wall and the FBs is a critical step in 2D flume tests. However, research on the effect of the gap on the accuracy of 2D FB experimental results is scarce. To address this issue, a numerical wave tank is developed using CFD to estimate the wave-FB interaction of a moored dual-cylindrical FB, and the results are compared to experimental data from a previously published work. There is good agreement between them, indicating that the numerical model is sufficiently accurate. The numerical model is then applied to explore the effect of gap diffraction on the performance of FBs in 2D experiments. It was discovered that the nondimensional gap length LGap/WPool should be smaller than 7.5% to ensure that the relative error of the transmission coefficient is smaller than 3%. The influence of the gap is also related to the entering wave properties, such as the wave height and period.
2024, 38(4): 676 -688
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0053-7
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
The Submerged Floating Tunnel (SFT) relies on a tensioned mooring system for precise positioning. The sudden breakage of a single cable can trigger an immediate alteration in the constraint conditions of the tube, inducing a transient heave response within the structure along with a transient increase in cable tension experienced by adjacent cables. In more severe cases, this may even lead to a progressive failure culminating in the global destruction of the SFT. This study used ANSYS/AQWA to establish a numerical model of the entire length SFT for the hydrodynamic response analysis, and conducted a coupled calculation of the dynamic responses of the SFT-mooring line model based on OrcaFlex to study the global dynamic responses of the SFT at the moment of cable breakage and the redistribution of cable internal forces. The most unfavorable position for SFT cable breakage was identified, the influence mechanism of cable breakage at different positions on the global dynamic response was revealed, and the progressive chain failure pattern caused by localized cable breakage are also clarified.
The Submerged Floating Tunnel (SFT) relies on a tensioned mooring system for precise positioning. The sudden breakage of a single cable can trigger an immediate alteration in the constraint conditions of the tube, inducing a transient heave response within the structure along with a transient increase in cable tension experienced by adjacent cables. In more severe cases, this may even lead to a progressive failure culminating in the global destruction of the SFT. This study used ANSYS/AQWA to establish a numerical model of the entire length SFT for the hydrodynamic response analysis, and conducted a coupled calculation of the dynamic responses of the SFT-mooring line model based on OrcaFlex to study the global dynamic responses of the SFT at the moment of cable breakage and the redistribution of cable internal forces. The most unfavorable position for SFT cable breakage was identified, the influence mechanism of cable breakage at different positions on the global dynamic response was revealed, and the progressive chain failure pattern caused by localized cable breakage are also clarified.
2024, 38(4): 689 -700
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0054-6
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Salter’s duck, an asymmetrical wave energy converter (WEC) device, showed high efficiency in extracting energy from 2D regular waves in the past; yet, challenges remain for fluctuating wave conditions. These can potentially be addressed by adopting a negative stiffness mechanism (NSM) in WEC devices to enhance system efficiency, even in highly nonlinear and steep 3D waves. A weakly nonlinear model was developed which incorporated a nonlinear restoring moment and NSM into the linear formulations and was applied to an asymmetric WEC using a time domain potential flow model. The model was initially validated by comparing it with published experimental and numerical computational fluid dynamics results. The current results were in good agreement with the published results. It was found that the energy extraction increased in the range of 6% to 17% during the evaluation of the effectiveness of the NSM in regular waves. Under irregular wave conditions, specifically at the design wave conditions for the selected test site, the energy extraction increased by 2.4%, with annual energy production increments of approximately 0.8 MWh. The findings highlight the potential of NSM in enhancing the performance of asymmetric WEC devices, indicating more efficient energy extraction under various wave conditions.
Salter’s duck, an asymmetrical wave energy converter (WEC) device, showed high efficiency in extracting energy from 2D regular waves in the past; yet, challenges remain for fluctuating wave conditions. These can potentially be addressed by adopting a negative stiffness mechanism (NSM) in WEC devices to enhance system efficiency, even in highly nonlinear and steep 3D waves. A weakly nonlinear model was developed which incorporated a nonlinear restoring moment and NSM into the linear formulations and was applied to an asymmetric WEC using a time domain potential flow model. The model was initially validated by comparing it with published experimental and numerical computational fluid dynamics results. The current results were in good agreement with the published results. It was found that the energy extraction increased in the range of 6% to 17% during the evaluation of the effectiveness of the NSM in regular waves. Under irregular wave conditions, specifically at the design wave conditions for the selected test site, the energy extraction increased by 2.4%, with annual energy production increments of approximately 0.8 MWh. The findings highlight the potential of NSM in enhancing the performance of asymmetric WEC devices, indicating more efficient energy extraction under various wave conditions.
2024, 38(4): 701 -710
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0055-5
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
The previous study conducted by Li (2022) demonstrates that the Goda graph can be adequately represented by a solitary-wave-like form across the entire range of relative water depth, with the exception of the extremely shallow zone. However, it remains uncertain whether this form is equally effective when applied to test data generated by irregular waves, as the Goda graph was initially developed based on overtopping data from regular wave tests. Additionally, it is unclear whether this form is suitable for formulating overtopping discharge at composite vertical walls. In order to address these questions, a 2D overtopping experiment was conducted, incorporating both simple and composite types of vertical walls, with various relative water depths across the entire range, excluding the extremely shallow zone. A novel analysis procedure was developed, which proved to be highly productive and can be considered a general method for data fitting. Ultimately, the study yielded two conclusions: (1) the solitary-wave-like form is remarkably effective in formulating overtopping test data generated by irregular waves, regardless of whether the vertical wall is simple or composite, and (2) the resulting formulas exhibit definitely better performance compared with existing formulas.
The previous study conducted by Li (2022) demonstrates that the Goda graph can be adequately represented by a solitary-wave-like form across the entire range of relative water depth, with the exception of the extremely shallow zone. However, it remains uncertain whether this form is equally effective when applied to test data generated by irregular waves, as the Goda graph was initially developed based on overtopping data from regular wave tests. Additionally, it is unclear whether this form is suitable for formulating overtopping discharge at composite vertical walls. In order to address these questions, a 2D overtopping experiment was conducted, incorporating both simple and composite types of vertical walls, with various relative water depths across the entire range, excluding the extremely shallow zone. A novel analysis procedure was developed, which proved to be highly productive and can be considered a general method for data fitting. Ultimately, the study yielded two conclusions: (1) the solitary-wave-like form is remarkably effective in formulating overtopping test data generated by irregular waves, regardless of whether the vertical wall is simple or composite, and (2) the resulting formulas exhibit definitely better performance compared with existing formulas.
2024, 38(4): 711 -724
doi: 10.1007/s13344-024-0056-4
[Abstract](0)
Abstract:
Ocean waves and Stokes drift are generated by typhoons. This study investigated the characteristics of ocean waves and wave-induced Stokes drift and their effects during Typhoon Mangkhut using European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA5 datasets and observational data. The results revealed that the typhoon generated intense cyclones and huge typhoon waves with a maximum wind speed of 45 m/s, a minimum pressure of 955 hPa, and a maximum significant wave height of 12 m. The Stokes drift caused by typhoon waves exceeded 0.6 m/s, the Stokes depth scale exceeded 18 m, and the maximum Stokes transport reached 6 m2/s. The spatial distribution of 10-m wind speed, typhoon wave height, Stokes drift, Stokes depth, and Stokes transport during the typhoon was highly correlated with the typhoon track. The distribution along the typhoon track showed significant zonal asymmetry, with greater intensity on the right side of the typhoon track than on the left side. These findings provide important insights into the impact of typhoons on ocean waves and Stokes drift, thus improving our understanding of the interactions between typhoons and the ocean environment. This study also investigated the contribution of Stokes transport to the total net transport during typhoons using Ekman-Stokes Numbers as a comparative measure. The results indicated that the ratio of Stokes transport to the total net transport reached up to 50% within the typhoon radius, while it was approximately 30% outside the radius. Strong Stokes transport induced by typhoon waves led to divergence in the transport direction, which resulted in upwelling of the lower ocean as a compensation current. Thus, Stokes transport played a crucial role in the vertical mixing of the ocean during typhoons. The findings suggested that Stokes transport should be paid more attention to, particularly in high latitude ocean regions, where strong winds can amplify its effects.
Ocean waves and Stokes drift are generated by typhoons. This study investigated the characteristics of ocean waves and wave-induced Stokes drift and their effects during Typhoon Mangkhut using European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA5 datasets and observational data. The results revealed that the typhoon generated intense cyclones and huge typhoon waves with a maximum wind speed of 45 m/s, a minimum pressure of 955 hPa, and a maximum significant wave height of 12 m. The Stokes drift caused by typhoon waves exceeded 0.6 m/s, the Stokes depth scale exceeded 18 m, and the maximum Stokes transport reached 6 m2/s. The spatial distribution of 10-m wind speed, typhoon wave height, Stokes drift, Stokes depth, and Stokes transport during the typhoon was highly correlated with the typhoon track. The distribution along the typhoon track showed significant zonal asymmetry, with greater intensity on the right side of the typhoon track than on the left side. These findings provide important insights into the impact of typhoons on ocean waves and Stokes drift, thus improving our understanding of the interactions between typhoons and the ocean environment. This study also investigated the contribution of Stokes transport to the total net transport during typhoons using Ekman-Stokes Numbers as a comparative measure. The results indicated that the ratio of Stokes transport to the total net transport reached up to 50% within the typhoon radius, while it was approximately 30% outside the radius. Strong Stokes transport induced by typhoon waves led to divergence in the transport direction, which resulted in upwelling of the lower ocean as a compensation current. Thus, Stokes transport played a crucial role in the vertical mixing of the ocean during typhoons. The findings suggested that Stokes transport should be paid more attention to, particularly in high latitude ocean regions, where strong winds can amplify its effects.
ScholarOne Manuscripts Log In
Current Issue

- Volume 38
- Issue 4
- September 2024
- Editor-in-Chief:
- Superintended by:
CHINA ASSOCIATION FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- Sponsored by:
Chinese Ocean Engineering Society (COES)
- Edited by:
Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute
Highlights
Stay up to Date







 Article abstracts by RSS
Article abstracts by RSS E-mail Alerts
E-mail Alerts